Losing access to your email data can disrupt your business. Contracts, client communications, and compliance records are at risk without a reliable backup and recovery plan. Here’s the key takeaway: cloud providers like Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace don’t fully back up your data. You’re responsible for securing, retaining, and recovering it.
Key Points:
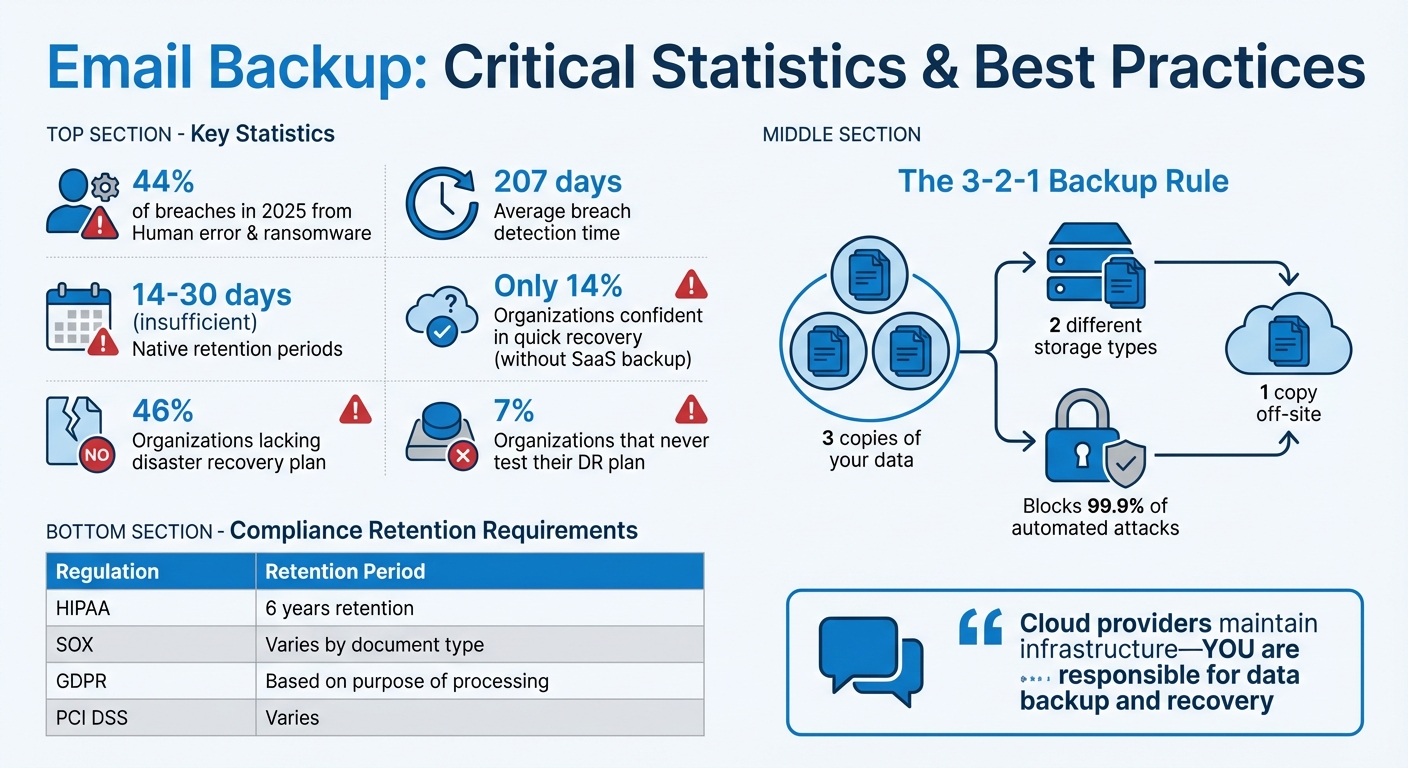
- Human error is the leading cause of data loss, followed by ransomware (44% of breaches in 2025).
- Cloud providers operate on a shared responsibility model - they maintain infrastructure, but your data is your responsibility.
- Native tools have limited retention periods (14-30 days), insufficient for long-term needs or unnoticed issues (average detection time: 207 days).
- 3-2-1 Backup Rule: Keep three copies of your data, on two different storage types, with one copy off-site.
- Use third-party tools like Veeam or Acronis for air-gapped backups, granular recovery, and extended retention.
Solutions:
- Regularly audit backups to ensure coverage for all accounts, including shared mailboxes and Teams chats.
- Encrypt backups, enforce role-based access, and comply with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR.
- Test recovery processes monthly to ensure backups are functional and meet recovery objectives.
Without proper backups, recovery could take weeks - or fail entirely. A solid plan ensures business continuity and compliance while protecting critical data.
Email Backup Statistics and Best Practices Overview
What Are The Best Email Disaster Recovery Practices? - TheEmailToolbox.com
Problem 1: Inconsistent or Incomplete Email Backups
A lot of businesses assume their cloud provider has them fully covered when it comes to email backups. Unfortunately, this assumption often leads to trouble. For example, backup scopes might not get updated when new employees join the team, or important items like shared mailboxes and Teams chats might be left out entirely. Even worse, storing backups in the same cloud environment as your primary data creates a single point of failure. If your Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace account gets hit with ransomware or unauthorized changes, both your main data and its backup could be wiped out. To avoid these pitfalls, a solid backup plan - like the 3-2-1 rule - can make all the difference.
Apply the 3-2-1 Backup Rule to Your Email System
The 3-2-1 rule is simple but effective: keep three copies of your data, store them on two different types of storage, and make sure one copy is kept off-site. For email systems, your first copy is your live production mailbox. The second copy could be a local backup, like a PST file saved on a departmental server. The third copy should be an air-gapped backup stored outside your main cloud provider’s environment.
Using an air-gapped backup from a third-party provider - such as Veeam, Acronis, or CloudAlly - ensures you have a clean recovery point, even if your primary account is compromised.
Use Built-In Features and Third-Party Backup Tools
Take advantage of built-in tools like Microsoft 365 Retention Policies or Litigation Holds through Microsoft Purview. These features can help prevent permanent email deletion beyond the standard 14-day window. However, keep in mind that Microsoft's native backup services are limited to a one-year retention period. For Google Workspace, tools like Google Vault allow you to set retention rules for Gmail and Drive, though it's primarily designed for legal discovery. Additionally, Google's Data Export tool provides a domain-wide backup option, but only once every 30 days.
When native tools fall short, third-party solutions can step in to fill the gaps. Tools like Acronis, Dropsuite, and MSP360 connect directly to your Microsoft 365 or Google Workspace account via API, automatically backing up all mailboxes - including shared ones and archives - to independent cloud storage. These services typically charge per user on a monthly basis.
Once you've selected the right tools, the next step is deciding what to back up and how often.
Set Your Backup Scope and Schedule
Not every mailbox needs the same level of backup protection. Start by identifying critical accounts - like those used by executives, HR, legal, and finance teams - and schedule more frequent backups for them. Define your Recovery Point Objective (RPO) to determine how much data loss is acceptable. For most businesses, a daily backup schedule works fine, but high-activity environments might need continuous or twice-daily backups.
To ensure your backup scope stays up to date, use dynamic rules. In Microsoft 365, you can set policies based on distribution lists or security groups, so new users are automatically included in backups. Regularly audit your backup coverage to catch any gaps, making sure shared mailboxes and Teams chats are part of the plan.
Problem 2: Slow or Limited Email Recovery
A backup is only as good as its ability to restore data quickly when needed. Many organizations face a harsh reality when they try to retrieve a single deleted email and end up restoring entire databases instead. This issue becomes even more frustrating when native cloud tools fall short on point-in-time recovery. In fact, only 14% of organizations without dedicated SaaS backups feel confident they can restore data within minutes of an incident. The situation worsens with traditional backup methods like tape or disk, which can create bottlenecks as data is transferred from backup servers to live systems.
"A backup that you can't successfully restore is no backup at all." - GoCorpTech
While tools like Recycle Bin or Trash allow quick recovery for recently deleted items, their retention periods - typically 14 to 30 days - are often inadequate for issues that go unnoticed for longer. Additionally, logical corruption in email systems can replicate across backups, forcing organizations into time-consuming rollbacks to restore earlier, uncorrupted states. This highlights the importance of having precise, granular recovery options.
Set Up Item-Level Recovery
Restoring individual emails, folders, or attachments without disrupting the entire system is essential for minimizing downtime. For Exchange Online, enabling single-item recovery ensures purged items remain retrievable in a hidden folder. On-premises or hybrid environments can use recovery databases to extract specific data without interrupting live operations. Admins can also extend the default 14-day retention period to 30 days through settings.
Third-party cloud-to-cloud backup solutions make recovery even easier. They provide granular search filters - by date, sender, folder, or item type - so you can quickly pinpoint and restore exactly what’s needed. These solutions also support point-in-time snapshots, allowing you to restore mailboxes to their exact state on a specific date, something native tools typically lack.
Here’s a real-world example: In October 2025, a 20-person architecture firm using Microsoft 365 faced a malicious deletion incident when a disgruntled employee purged project folders from SharePoint. Thanks to a third-party backup solution, the administrator restored all deleted data within an hour, avoiding what could have been a catastrophic loss after the 93-day native retention period expired.
Create Written Recovery Procedures
Even with granular recovery options, having clear, actionable procedures is critical. A well-documented Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) ensures your team knows exactly what to do during incidents. This plan should include key contacts, activation protocols, and step-by-step recovery instructions for various scenarios - whether it’s a ransomware attack, accidental deletion, or account compromise.
For example, your DRP should outline specific steps for restoring data in Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace, covering tasks like accessing Recovery Databases, using eDiscovery tools, or initiating third-party backup restores. 46% of businesses lack a documented disaster recovery plan, and among those that do, 7% never test their protocols. Without written procedures, recovery times can stretch as IT teams scramble to figure out the process under pressure.
Your documentation should also address recovery destinations. Specify whether data should be restored in-place (overwriting current data) or to a new location (preserving existing data while recovering older versions). This clarity eliminates guesswork and sets the foundation for smooth recovery operations.
Run Regular Recovery Tests
Testing your recovery process is just as important as having a backup. Regular drills - monthly or quarterly - help verify backup integrity, measure recovery speed, and uncover any gaps in your disaster recovery plan. These tests should include restoring individual emails, entire mailboxes, and shared folders to ensure your team is well-versed in the process.
If you’re using Microsoft 365 Backup, limit testing to twice a month per protection unit to avoid being flagged for excessive activity. When available, use "express" restore points for faster performance during full account or site recoveries. Track your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) - the maximum acceptable downtime - and Recovery Point Objective (RPO) - the maximum acceptable age of data loss - during each test to ensure your setup aligns with business needs.
| Recovery Method | Speed/Efficiency | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Recycle Bin/Trash | Fast (Seconds) | Immediate recovery of recently deleted items |
| Recovery Database | Moderate | Extracting specific data without disrupting live users |
| Dial Tone Recovery | Fast (for service) | Maintaining business continuity during major database failures |
| 3rd-Party Cloud Restore | Very Fast | Granular, point-in-time recovery of items or full mailboxes |
Problem 3: Security and Compliance Risks in Email Backups
Recovering data quickly is essential to minimize downtime, but ensuring the security of your backup data is just as critical to protect sensitive information.
Email backups often contain highly sensitive data, including customer details, financial records, and intellectual property. Unfortunately, many organizations fail to secure this data properly, leaving it vulnerable to threats such as unencrypted storage and weak access controls. According to the 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report, ransomware was involved in 44% of breaches investigated. Attackers increasingly target backup systems to block recovery efforts. Without adequate security, these backups can turn into liabilities, exposing businesses to data breaches and regulatory penalties.
The ramifications go beyond the loss of data. Healthcare organizations risk HIPAA violations, financial institutions face SOX non-compliance, and any business handling customer data may be subject to breach notification laws. For example, a health insurer had to settle for $115 million after a breach caused by spear-phishing exposed unencrypted backup data. When backups lack encryption, access controls, and proper retention policies, the risks extend far beyond data loss. Regulatory fines can be severe, such as $50,000 per HIPAA violation, with annual penalties exceeding $2 million.
Encrypt Your Backup Data
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to secure backups from unauthorized access, whether the data is at rest or in transit. Implement 256-bit AES encryption to comply with HIPAA requirements and reduce the risk of breaches. Without encryption, a compromised server or stolen hard drive could expose every email, attachment, and conversation stored within.
"Encryption is the primary method of achieving [transmission security] for data in motion and data at rest." - ASHA
For added protection, use customer-managed keys (CMK) stored separately from the backup data. This approach ensures you maintain full control over the encryption keys, though it’s essential to include these keys in your backup plan to avoid permanent data loss. Additionally, use private endpoints within a virtual network to keep backup traffic off public networks, adding another layer of security.
Control Access with Role-Based Permissions
Restricting access to backup systems is key to preventing both external attacks and insider threats. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) ensures that only authorized individuals can perform critical tasks such as modifying retention policies or restoring data. Assign roles like Backup Operator for daily monitoring, Backup Reader for compliance checks, and Backup Contributor for managing policies to enforce the principle of least privilege.
One healthcare organization, facing HIPAA compliance challenges, implemented Azure RBAC to separate duties between Backup Operators and Backup Contributors. During a ransomware attack, multi-factor authentication (MFA) and multi-user authorization prevented unauthorized deletion of backups. These measures ensured recoverable backups remained intact throughout the incident.
Require MFA for all high-impact actions, such as restoring backups or changing retention policies. For particularly sensitive operations - like disabling immutability or reducing retention periods - use multi-user authorization (MUA), which requires a second user’s approval. Enable soft delete features to retain deleted backup data for 14 days, creating a recovery window even if initial access controls are bypassed.
Match Retention Policies to Legal Requirements
Different regulations require varying retention periods, and non-compliance can lead to costly penalties. For instance, HIPAA mandates that healthcare organizations retain records for six years, while SOX requires tamper-proof archiving for financial documents. Ensure your backup system enforces retention rules that align with these timelines.
Use Litigation Hold features to preserve user data immutably for legal discovery. This ensures emails related to legal cases cannot be altered or deleted. Litigation Holds must also maintain a tamper-proof chain of custody, providing evidential-quality data. If you’re using third-party providers for HIPAA-regulated data, it’s crucial to execute a Business Associate Agreement (BAA) to ensure compliance.
| Regulation | Key Requirement for Email Backups | Typical Retention Period |
|---|---|---|
| HIPAA | Access control, audit logs, and data integrity | 6 Years |
| SOX | Tamper-proof archiving and eDiscovery | Varies by document type |
| GDPR | Secure storage, data protection, and erasure rights | Based on "purpose of processing" |
| PCI DSS | Data encryption and restricted access | Varies |
Once the retention period expires or legal obligations are fulfilled, automate the deletion process using multi-administrator authorization and activity logs to permanently remove emails. This approach helps manage data storage efficiently while adhering to data minimization principles. Legal expenses during litigation can also be reduced - manual review accounts for nearly 70% of total email discovery costs. Automated culling and deduplication features in your backup system can significantly ease this burden.
sbb-itb-6e7333f
Problem 4: Process Failures in Backup Management
When it comes to backup strategies, operational missteps can render even the best plans useless. Many organizations only realize their backups have been failing for weeks - or worse, discover that critical data left with a departing employee - when it’s too late. These issues often arise from poor monitoring, weak integration with user management systems, and insufficient training for staff.
The fallout? Costly downtime and a high rate of failed data recoveries. What’s worse, detecting data changes can take months. By the time the problem is identified, the typical 14–30 day retention window has passed, leaving recovery impossible.
Set Up Backup Monitoring and Alerts
Failed backups are one of the easiest causes of data loss to avoid - yet they’re also among the most common. Without real-time monitoring, these failures often go unnoticed until you need the data. That’s why it’s critical to set up immediate alerts for failed jobs, storage shortages, or unusual activity. Tools like Azure Backup Center can help by offering a centralized view of all backup tasks.
"A backup is only as good as its ability to be restored, and yet, many organizations assume their backups will work without ever testing them." - Colin Hanks, Sr. Product Marketing Manager, Veeam
To ensure your backups are reliable, automate recoverability checks and schedule monthly tests to evaluate recovery speed and data integrity. Solutions like SureBackup can verify the restorable state of your backups automatically, reducing the risk of unpleasant surprises during a crisis. Set up multi-channel notifications - via email, ITSM systems, or webhooks - so critical alerts reach the right people without delay. For continuous oversight, consider integrating backup monitoring with your Network Operations Center (NOC).
Connect Backup Policies to User Management Systems
One of the most damaging failures in backup management happens during employee offboarding. When a user’s license is revoked, their data is often deleted permanently after 30 days. If that data hasn’t been backed up or archived, it’s gone for good. This problem arises when backup policies are disconnected from identity management systems.
"Microsoft is responsible for ensuring service availability... You are responsible for the data that lives within Microsoft 365. This includes emails, attachments, calendars, and more." - Kendall Gray, Product Marketing Associate, Veeam
To address this, integrate your backup system with directory services like Active Directory. This allows new users to be automatically assigned protection policies upon onboarding. You can also use resource tagging - like assigning a “BackupTier: Gold” tag - to ensure retention and frequency settings match a user’s role or department. For departing employees, require a full backup or migration to an immutable archive before deactivating their account. Use features like Litigation Hold or Inactive Mailboxes to preserve data beyond the standard deletion window, especially for compliance needs.
Once these processes are automated, the next step is ensuring your team knows how to manage them effectively.
Train Staff on Backup Procedures
Even with robust monitoring and automation, your staff plays a key role in maintaining backup integrity. Automated systems are only as effective as the people managing them.
Without proper training, backup jobs can be missed, and there’s often a dangerous assumption that service providers handle more than they actually do. Manual errors - like skipping scheduled backups, mislabeling datasets, or accidentally deleting files - are common. In fact, nearly half of failed software and backup deployments stem from incorrect initial setups.
Educate your IT team on the fundamentals of backup management. Emphasize that while service providers manage infrastructure, your organization is responsible for data retention and recovery. Teach staff to spot potential threats, such as mass file changes that may indicate ransomware. Limit access to backup management with Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to prevent accidental deletions. Additionally, collaborate with business unit managers to document and negotiate Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) well before any crisis occurs.
| Failure Type | Early Identification Method | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Failed Backup Job | Automated real-time alerts | Policy-based automation |
| Human Error | Audit logs and access monitoring | Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) |
| Configuration Drift | Baseline deviation alerts | Standardized policy templates |
| Data Corruption | Automated restore drills | 3-2-1-1-0 Backup Rule |
| Offboarding Loss | User management system triggers | Automated archiving workflows |
Problem 5: Selecting Email Services and Backup Solutions That Scale
Picking the wrong email platform or backup solution can cost more than just money - it can cost you your data. Many businesses only realize their backup systems are inadequate when they face rapid growth, changing compliance demands, or the challenges of managing distributed teams across multiple time zones. The real challenge? Finding a solution that not only works today but also keeps up as your business grows.
And the risks are real. Over half of organizations have experienced cloud data loss due to malicious deletions, while one-third have lost data because of accidental deletions. To make matters worse, only 14% of businesses without proper SaaS backups feel confident they could recover data within minutes of an incident. To avoid these pitfalls, it’s crucial to establish clear, informed criteria when selecting a solution.
Key Features to Look For
When evaluating backup solutions, prioritize features that ensure flexibility and reliability as your business scales. Here are a few must-haves:
- Granular recovery: The ability to restore individual emails instead of entire mailboxes saves time and minimizes disruption.
- Air-gapped storage: Backups stored in an independent cloud environment protect against system-wide compromises.
- Automated scaling: Solutions that automatically detect and protect new users and data sources ensure seamless growth.
- Self-service restore options: These empower teams to recover data remotely without waiting for IT support.
- Data sovereignty options: Storing backups in specific regions helps meet compliance requirements.
Security is equally important. Encrypted backups with strong access controls, such as Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), can block 99.9% of automated attacks. If you work in sensitive industries like defense, finance, or government, look for FIPS 140-2 encryption support. Additionally, immutable storage - backups that can’t be altered or deleted, even by administrators - provides an extra layer of protection against ransomware.
| Feature | Why It Matters for Scaling |
|---|---|
| Automated User Detection | Ensures new users are covered as teams grow |
| Air-Gapped Storage | Shields data from system-wide breaches |
| Granular Recovery | Speeds up recovery by restoring specific items |
| Data Sovereignty | Meets regional compliance requirements |
| Immutable Backups | Protects against ransomware and unauthorized changes |
Define Your Recovery Goals
Before diving into vendor evaluations, define your Recovery Time Objective (RTO) and Recovery Point Objective (RPO). These metrics are vital for aligning solutions with your business needs:
- RTO: How quickly do you need systems to be back online?
- RPO: What’s the maximum amount of data you can afford to lose?
For example, a retail business might need systems restored within minutes, while a law firm might prioritize near-zero data loss over speed. Clearly outlining these objectives will help narrow your options and ensure you choose a solution that meets your operational demands.
Simplify Vendor Comparison
The Email Service Business Directory can make your search easier. This resource aggregates top tools, software, and service providers, allowing you to compare features, pricing, and compliance capabilities side-by-side.
Whether you’re managing transactional emails for an e-commerce platform or running data-driven campaigns for a SaaS company, the directory can help you find a solution tailored to your needs. It also offers filters for backup solutions, letting you sort by retention periods, storage independence, and automation features - minimizing the risk of choosing a solution that won’t scale with your business.
Find the Right Fit for Your Business
Ultimately, your decision should align with your organization’s size, budget, and compliance needs. For smaller businesses with fewer than 50 employees, a cloud-to-cloud solution priced per user might be sufficient. Larger enterprises, on the other hand, may benefit from hybrid setups that combine cloud and on-premises storage for faster local recovery.
When weighing options, consider the total cost of ownership. This includes not just subscription fees but also potential losses from data breaches. While third-party solutions may cost more upfront, they often provide advanced features - like unlimited retention and air-gapped storage - that native tools lack.
Compliance is another critical factor. If your business is subject to regulations like HIPAA, PCI-DSS, or GDPR, you’ll need solutions that meet specific requirements. For instance:
- HIPAA: Requires retrievable copies of electronic protected health information (ePHI) with six-year retention periods.
- PCI-DSS: Demands secure storage of cardholder data.
- GDPR: Mandates measures for data protection and the ability to delete personal data upon request.
For distributed teams, look for features like role-based access control (RBAC) and geolocation tracking for remote hardware. If your team operates internationally, ensure the provider can store data in designated regions to comply with local residency laws. And don’t forget to test the recovery process under different conditions to confirm the solution can handle real-world scenarios without bottlenecks.
Test Before You Commit
Before signing any contracts, request a trial period. Use this time to run restore drills with actual data, simulating growth scenarios like adding 100 new users in a month. This will help you confirm that the solution can scale effectively and protect your data as your business evolves.
"A backup that you can't successfully restore is no backup at all." - GoCorpTech
Conclusion: Building Reliable Email Backup and Recovery Systems
Backing up email data isn't just a good idea - it's a must-have for any business. Many organizations face data loss due to accidental or malicious deletions, and relying solely on cloud providers like Microsoft or Google won’t cut it. Under the shared responsibility model, these providers ensure their infrastructure runs smoothly, but safeguarding and recovering your data? That’s on you. And with native tools offering retention windows of just 14–30 days, they fall short when it takes an average of 207 days to even notice unintended data changes.
A solid backup plan should follow the 3-2-1 rule: keep three copies of your data, store them on two different types of storage, and ensure one is off-site. To strengthen this, add encrypted storage, automated monitoring, and regular recovery tests to make sure your backups are ready when you need them most. As GoCorpTech aptly states:
A backup that you can't successfully restore is no backup at all.
This principle lies at the heart of a dependable backup system.
Once your practices are in place, selecting the right vendor becomes crucial. Features like immutable storage, granular recovery options, and role-based access control are vital for any robust solution. To simplify the search, the Email Service Business Directory offers a side-by-side comparison of vendors. You can filter options by retention policies, compliance certifications, or automation tools, making it easier to find a solution tailored to your needs. Whether you’re looking for HIPAA-compliant storage with a Business Associate Agreement or a scalable solution for a growing team, this directory takes the guesswork out of finding the right fit.
FAQs
What is the 3-2-1 backup rule, and why is it important for email systems?
The 3-2-1 backup rule is a trusted method for protecting email systems and other important data. Here's how it works: you maintain three copies of your data, use two different types of storage media, and ensure one copy is stored off-site.
This strategy shields your email data from threats like accidental deletions, hardware malfunctions, ransomware, or even natural disasters. By sticking to the 3-2-1 rule, businesses can minimize disruptions, stay compliant, and keep operations running smoothly when unexpected issues arise.
What are the risks of depending only on built-in cloud backup tools?
Relying only on the built-in backup tools provided by cloud services can expose your business to a range of risks. These tools often come with limited protection capabilities and might not offer strong defenses against service disruptions or data corruption. Plus, most cloud providers operate under a shared-responsibility model. This means while they manage the infrastructure, the responsibility for safeguarding and recovering your email data falls on your organization.
Without a more robust backup solution, you could miss out on critical features like advanced malware protection, extended data retention, and compliance support. These are essential for meeting regulatory standards and maintaining smooth business operations.
What steps can I take to ensure my email backups comply with regulations like HIPAA or GDPR?
To make sure your email backups align with HIPAA or GDPR requirements, it's essential to view the backup process as a key part of your overall data protection strategy.
For HIPAA compliance, start by determining whether you're a covered entity or a business associate. If you're working with a third-party backup provider, ensure they sign a Business Associate Agreement (BAA). Your backups should include encryption (both during transfer and while stored), strict access controls, and comprehensive audit logs. Regular risk assessments are critical - identify where sensitive data is stored, implement role-based permissions, and confirm the reliability of your backups by performing test restores on a routine basis.
When it comes to GDPR compliance, similar precautions apply. Encrypt your email archives, restrict access to authorized individuals, and maintain thorough documentation of data processing activities. Backups should be stored in regions with sufficient data protection measures or transferred using approved mechanisms. It's also vital to retain data only for as long as legally required and to clearly define your retention policies. Tools like the Email Service Business Directory can help you identify backup providers that meet these compliance criteria, streamlining the process of choosing vendors and managing agreements.