Customizing email templates in Drupal allows you to transform plain-text emails into branded, visually appealing messages that match your website's design. This process involves adding logos, colors, and HTML formatting to enhance both the appearance and functionality of your emails. Here's how you can do it:
Key Steps:
-
Install Required Modules:
- Use
Mail Systemfor formatting and sending emails. - Choose between
Mime MailorSymfony Mailerfor HTML email support. - Run
composer require drupal/mailsystem drupal/mimemailto install.
- Use
-
Configure Modules:
- Set up Mime Mail at
/admin/config/system/mimemailfor HTML processing. - Use Mail System to manage email formatting and delivery.
- Set up Mime Mail at
-
Add Custom CSS:
- Create a
mail.cssfile in your theme directory for email-specific styles. - Use table-based layouts and inline styles for compatibility with email clients.
- Create a
-
Customize Email Templates:
- Copy and edit the base
mimemail-message.html.twigfile in your theme. - Add branding elements like headers, footers, and logos.
- Override templates for specific modules or email types as needed.
- Copy and edit the base
-
Test Across Email Clients:
- Use tools like Mailhog, Putsmail, or Litmus to preview emails and ensure email platform compatibility.
- Keep email size under 102KB to avoid clipping in Gmail.
Customizing your Drupal emails improves their design, ensures consistency with your brand, and creates a better experience for your users.
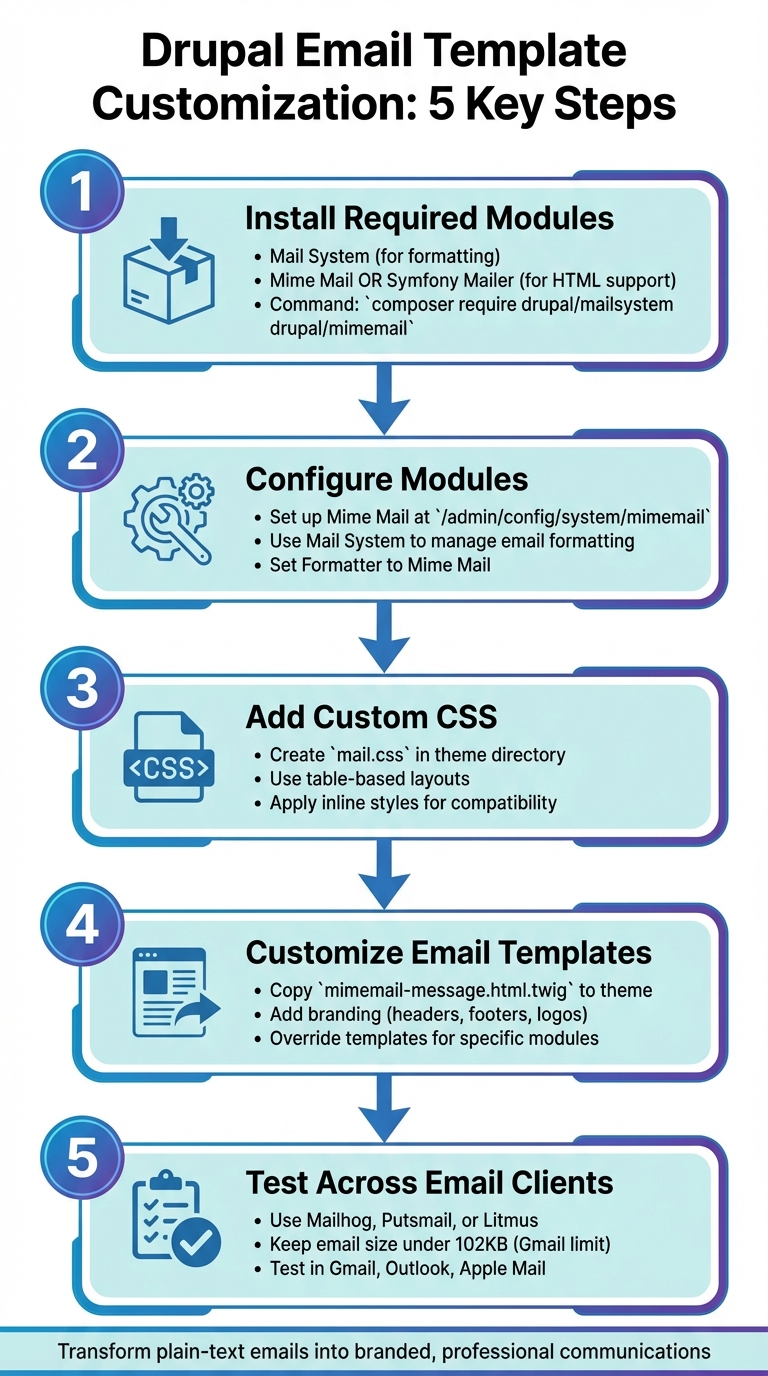
5 Steps to Customize Drupal Email Templates
HTML Emails from Drupal Made Easy: A walkthrough of the Easy Email module for Drupal
sbb-itb-6e7333f
What You Need Before Starting
Before diving into email customization, ensure you're using a supported version of Drupal and have the necessary modules and technical expertise. Since Drupal 7 officially reached its End of Life on January 5, 2025, you'll need to work with Drupal 8, 9, 10, or 11. These versions fully support the modules and systems required for customizing email templates. Setting up the right Drupal environment and permissions is crucial for a smooth experience throughout this process.
Drupal Version and Required Modules
To customize emails in Drupal, certain modules are essential. Key ones include Mail System (for email formatting), along with either Mime Mail or Symfony Mailer. Mime Mail is used by 51,694 sites as of early 2026, while Symfony Mailer has been adopted by 41,020 sites. Additionally, the HTML Mail module (version 4.0.x) integrates with your existing theming engine.
Here’s a quick breakdown of these modules:
- Mime Mail (v2.0.1): Supports Drupal 10.3 and 11.
- Symfony Mailer: A modern replacement for the now-unsupported Swiftmailer, offering deeper integration with Drupal theming.
For new installations on Drupal 10 or 11, Symfony Mailer is the recommended choice. As the Mailer Plus project notes:
"Symfony Mailer is not just another mail plug-in – rather it's a full mail system that replaces the one in Drupal Core".
Swiftmailer, unsupported since November 2021, is no longer a viable option for current projects. After setting up these modules, confirm that your technical environment meets the necessary skills and permissions outlined below. If you are still deciding on your overall strategy, you might want to compare email marketing platform questions to ensure Drupal is the right fit for your needs.
Required Skills and Access Permissions
To customize email templates, you'll need working knowledge of Twig, HTML, and CSS. You'll also need basic Composer skills and familiarity with Drupal's file structure. Administrative permissions are a must, along with secure file transfer access (via FTP or SSH) for configuring the Mail System module and uploading theme files.
Specifically, ensure you have the "Administer site configuration" permission to access settings for Mail System and Mime Mail. It's also a good idea to test changes in a local environment before pushing them live. Tools like Mailhog or DDEV can help intercept outgoing emails during testing, ensuring everything works as expected before deployment.
Installing and Setting Up Email Modules
After confirming your environment and permissions, it's time to install the modules needed for HTML email customization. You'll need both Mime Mail and Mail System, as Mime Mail relies on Mail System to work properly. To install them, run composer require drupal/mailsystem drupal/mimemail and then enable the modules through the admin interface or by using drush en mailsystem mimemail. Once installed, configure both modules to enable HTML email customization.
Setting Up Mime Mail
After installation, configure Mime Mail for handling HTML emails. Navigate to /admin/config/system/mimemail to adjust its settings. The key setting here is the default email text format - choose Full HTML to ensure proper HTML processing. If you're using a dedicated mail.css file, make sure to uncheck "Include site style sheets." For testing HTML formatting, you can use the Mime Mail Example submodule, accessible at /admin/config/system/mimemail/mimemail_example.
Setting Up Mail System Module
The Mail System module works as the backbone for managing your emails, handling two key functions: formatting (appearance) and sending (delivery). Configure it at /admin/config/system/mailsystem. Set the Formatter to Mime Mail and the Sender to PhpMail - or to SMTP Mailer if that's your preferred delivery method.
Be sure to set the "Theme to render the emails" to your active theme. Without this, template overrides won't apply. Once configured, the Mail System module ensures all outgoing emails are formatted through Mime Mail for HTML rendering before being sent via your chosen delivery method.
Adding Custom CSS to Email Templates
Custom CSS can transform Drupal's plain-text emails into something that aligns with your brand's design. The Mime Mail module makes this process straightforward by automatically looking for a file named mail.css in your active theme directory. Once detected, it applies those styles to your email template. This keeps your email-specific styles separate from your website's CSS, helping avoid any unexpected styling conflicts.
Creating a Mail-Specific CSS File
To get started, create a mail.css file in the root directory of your custom theme. Mime Mail will automatically apply the styles from this file to your email templates. Then, head over to /admin/config/system/mimemail and uncheck the Include site style sheets option.
When crafting your email CSS, keep it simple to ensure compatibility across various email clients. Stick to CSS 2.1 properties and avoid modern features like flexbox or grid since they often fail to work in clients like Outlook. Instead, lean on table-based layouts for structure, as they’re more reliable for email rendering. Also, use absolute URLs for images (e.g., https://example.com/logo.png) to ensure they display properly. Mime Mail automatically converts your CSS rules into inline styles before sending, boosting compatibility across email platforms [18][19][20][23].
"By default, Mime Mail will look for a mail.css file in your theme and will include it in your email template."
– Haley Troyer, UX Designer and Front-end Developer, Rapid Development Group
Once your CSS file is ready, it’s time to test how it performs across different email clients.
Testing Styles in Different Email Clients
Testing is crucial because email clients handle CSS differently. For local previews, tools like Mailpit [17] are handy for reviewing HTML emails. When you're ready to test on real clients, Putsmail is a free service that lets you send test emails to multiple addresses at once. For a deeper dive, platforms like Litmus or Email on Acid offer screenshots of how your email appears in various clients.
Don’t skip manual testing in major email clients like Gmail, Outlook, and Apple Mail. Each has its quirks, and catching rendering issues early can save you trouble later. Also, keep your email’s total HTML size under 102kb - Gmail clips emails exceeding this limit, which could hide important elements like unsubscribe links. Since Gmail removes <style> tags from the <head> section, inline styles (handled by Mime Mail) are essential for consistent appearance [19][20][24].
Building Custom HTML Email Templates
Customizing HTML email templates allows you to control the layout and branding of your emails. With Drupal's Mime Mail module, you can modify the base template, mimemail-message.html.twig (or mimemail-message.tpl.php in Drupal 7), to align with your brand. This template must include proper <html>, <head>, and <body> tags to ensure emails are well-formed and avoid delivery issues. Once you’ve set up your custom CSS, you can adjust the HTML structure to reflect your brand identity.
Copying and Editing Base Templates
Start by copying the default mimemail-message.html.twig file into your active theme's /templates directory. Within this template, you’ll find the {{ body|raw }} placeholder, which is essential for rendering the email content. Leave this placeholder intact, and add your branding elements, such as a header, footer, logo, or custom styles, around it.
For reliable rendering across email clients, stick to a table-based layout. Also, ensure all images use absolute URLs to avoid loading issues. After editing, clear the Drupal cache to apply your changes. Additionally, check that the "Theme to render the emails" setting at /admin/config/system/mailsystem is set to your active theme. If needed, you can extend these customizations for module-specific emails.
Overriding Templates for Specific Modules
To refine branding for specific emails, you can override templates for individual modules or email types. Drupal's template system uses a hierarchy that prioritizes more specific templates over general ones. For example, to customize a specific email type, create a file named mimemail-message--[module]--[key].html.twig in your theme's /templates folder. If no specific template is found, Drupal defaults to broader options.
Here’s a quick guide to the template hierarchy:
| Template Level | Filename Pattern | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Specific Email | mimemail-message--[module]--[key].html.twig |
For a specific notification, e.g., Password Reset |
| Module Level | mimemail-message--[module].html.twig |
Branding for all emails from a specific module |
| Global Level | mimemail-message.html.twig |
Default layout for all system-generated emails |
To identify the correct email key (e.g., password_reset), refer to the relevant module's documentation or source code (like user.module). Enabling Twig debug mode can also be helpful, as it shows the template suggestions Drupal uses when sending an email. Note that some modules, such as Webform, may use their own templates (e.g., webform-email-html.html.twig) instead of the Mime Mail base template.
Applying and Testing Your Custom Templates
Updating Default Email Templates
Once your custom templates are ready, you'll need to configure Drupal to use them. Head over to Configuration > System > Mail System (/admin/config/system/mailsystem) and set the Formatter to Mime Mail. Next, select the Theme to render the emails - this should be the active theme where your template files are located. This step ensures Drupal recognizes and applies your customizations.
Don't forget to clear Drupal's cache after making changes to the template files. If you're working with Webform emails, you can apply your custom templates directly through the Webform interface. Go to Webform > E-mails > Edit, then switch from "Default template" to "Custom template" to activate your changes.
Testing Email Delivery and Display
Testing is critical because email clients render HTML in different ways. Start by using tools like Mailpit to intercept outgoing emails locally [17]. This allows you to review the rendered HTML and confirm that your branding elements look as intended. To track outgoing emails directly in Drupal, enable the Helper module, which logs all emails under Reports > Recent log entries [33].
For broader compatibility testing, platforms like Putsmail or Litmus can be invaluable [31]. As Serhii Checheniev from Lemberg Solutions points out:
"Outlook desktop on Windows supports fewer features than on macOS. For example, you won't be able to use a CSS 'background-image' for Windows" [31].
To ensure your emails display well across devices, keep the width at 600 pixels or less. Also, keep your HTML optimized and under Gmail's 102KB limit, as emails exceeding this size may get clipped [28][29]. With thorough testing complete, you can confidently deploy your custom email templates.
Conclusion
Transforming plain-text emails into branded, professional communications is entirely achievable in Drupal. By using modules like Mime Mail and Mail System, crafting custom HTML templates, and applying CSS styling, you can take full control over how your site’s emails - like password resets, form confirmations, and account notifications - look and feel. This process not only enhances aesthetics but also boosts usability and user engagement.
Custom email templates go beyond just looking good. They ensure your brand remains consistent and recognizable across all touchpoints. With HTML support, you can include rich content, clickable links, and ensure compatibility across devices with inlined styles. Haley Troyer from Rapid Development Group highlights this importance:
"The design of these emails is therefore an important touchpoint that should not be forgotten about."
Drupal’s template hierarchy and token system provide the flexibility to design emails tailored to specific purposes while keeping the overall branding intact.
Once your custom templates are ready, thorough testing across email clients like Gmail and Outlook is essential. This step ensures your emails render correctly and deliver the polished experience you’ve worked to create.
FAQs
How can I make sure my email templates display correctly across all email clients?
To keep your email templates looking consistent across various email clients, it's best to stick with HTML 4.01 or XHTML 1.0 standards. Also, aim for an email width between 600 and 640 pixels - this range ensures your content is easy to read without unnecessary scrolling.
When it comes to layout, use tables instead of relying on CSS positioning. Why? Because many email clients have limited support for CSS, which can lead to broken designs.
Lastly, always test your emails on different email clients and devices. This step helps you catch any rendering issues early, so your design and functionality work smoothly for everyone.
What skills do I need to customize email templates in Drupal?
To create custom email templates in Drupal, you'll need a good grasp of HTML and CSS to design and style your templates properly. This includes incorporating branding, ensuring responsive layouts, and using inline styles to maintain compatibility across various email clients.
It's also essential to understand Drupal's module configuration and templating system. Tools like Mime Mail and Swiftmailer offer advanced customization options, so knowing how to configure these modules, override Twig templates, and embed custom styles is crucial. Familiarity with Drupal's admin interface for managing email settings can make the process smoother.
Additionally, having basic testing and debugging skills is important to ensure your templates look right on different email platforms. Using testing tools or local environments can help you quickly identify and fix issues with delivery or formatting. By combining these skills, you can create polished and functional email templates tailored to your requirements.
What are the benefits of using Symfony Mailer instead of Mime Mail in Drupal?
Symfony Mailer brings powerful tools to the table for crafting rich, tailored email templates in Drupal. It supports HTML emails, file attachments, and embedded images, enabling you to create polished, visually engaging emails that stand out.
On top of that, Symfony Mailer offers advanced delivery features like load balancing, email signing, and encryption. These capabilities ensure secure, reliable, and efficient email handling, making it a smart choice for businesses aiming to improve their email communication and branding.


